EEAP 2022: TFA yields from HFCs and HFOs
EEAP 2022 reviewed the yields of TFA from individual compounds, estimated based on evaluations of the available literature. These are shown in the figure reproduced in part from EEAP 2022 [1]. Error bars in the figure represent both experimental uncertainties and upper and lower yield ranges due to competing reaction channels that depend on environmental conditions.
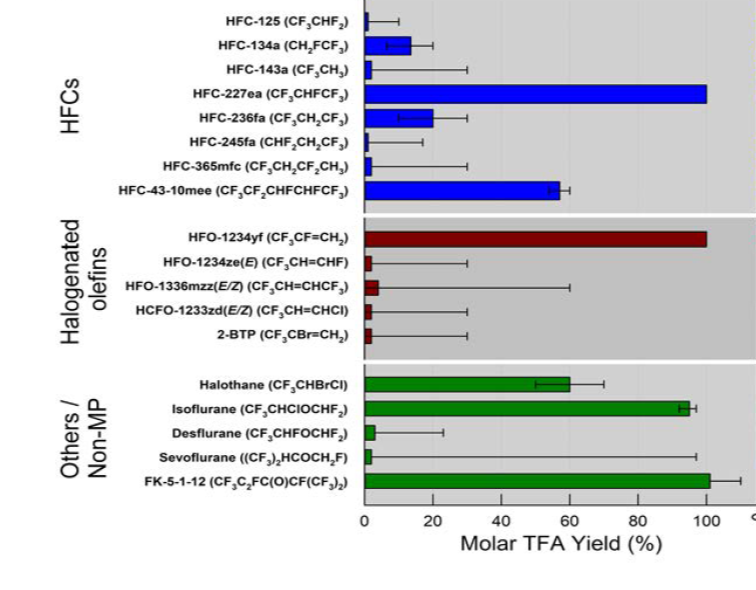
EEAP 2022 quotes estimated TFA yields for HFOs and HCFOs as: HFO-1234yf, 100%; HFO-1234ze(E), 2%; HFO-1336mzz(E/Z), 4%; HCFO-1233zd(E), 2%. HFO-1234ze(E), HFO-1336mzz(E/Z), and HCFO-1233zd(E) degrade in the atmosphere via CF3CHO. The yield of TFA from CF3CHO may depend on whether it remains in gaseous form. The reaction of OH radicals with the hydrated form of CF3CHO in the gas phase is known to be an effective route for formation of TFA (100%); however, to what extent CF3CHO could be removed from the atmosphere through wet scavenging and undergo multiphase chemistry is unknown. EEAP 2022 in the Chapter 6 Appendix [2] states “Thus, the TFA yield from processing of CF3CHO is estimated at 2% with an upper theoretical limit of ~ 30%.” The atmospheric degradation of HFC-143a, HFC-245fa and HFC-365mfc also has CF3CHO as an intermediate product. For HFC-125, a minor reaction pathway can lead to a low yield of TFA.
Notes
[1] EEAP 2022, Chapter 6, Figure 12 page 282
[2] EEAP 2022, Chapter 6, Appendix, SI 4 Estimated molar yields (%) of TFA from ODS replacements. Section SI 4.1.3 discusses CF3CHO, and the degradation of each substance is discussed.